What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?

Rheumatoid arthritis abbreviated as (RA) is a long-term chronic disease that causes inflammation of the joints. This inflammation can be so severe that it can potentially affect how the joints and other parts of the body look and function. In the hand, RA may cause deformities in the joints of the fingers. This makes moving your hands difficult. Lumps or bumps, known as rheumatoid nodules, may form anywhere in the body.
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) is a form of arthritis in children ages 16 or younger. It causes inflammation and joint stiffness that lasts for more than 6 weeks. Unlike adult RA, which lasts a lifetime, children often outgrow JRA. But the disease can affect bone development in a growing child.
What causes Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
RA is an autoimmune disorder that destroys its own tissues. The exact cause of it is unknown. By attacking its own healthy tissues, it causes inflammation in and around the joints which can lead to damage to the skeletal system. RA can also damage other organs such as the lungs and heart muscle. Recent research has linked RA to being hereditary and although it can occur at any age, it generally happens more in woman between the ages of 30 t0 50.
What are the symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
With RA, the joints of the hands, wrists, feet, ankles, knees, shoulders, and elbows are most affected. It causes swelling in the same areas on both sides of the body. The symptoms may be acute (happening suddenly) or chronic (slowly over time). The symptoms vary from person to person and may include pain and stiffness during the mornings, swelling over the affected joins, decreased mobility, pain that worsens with joint movement, lumps and bumps over small joints, difficulty doing ADL (Activities of daily living) such as combing hair, opening jars, tying shoes, and buttoning clothing, tiredness, and occasional fever. These symptoms can mimic other health conditions so it’s important to see a healthcare provider for a more accurate diagnosis.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis diagnosed?
Although early detections are important with most diseases and disorders, diagnosing RA can be difficult, especially in the early stages. This is mainly since some symptoms may be mild in the beginning and signs of disease may not be seen on x-rays or blood tests. Your primary care physician may take an extensive medical history and physical exam. They may also order other tests to rule out other diseases such as x-rays, joint aspirations, nodule biopsies, blood tests and ultrasounds.
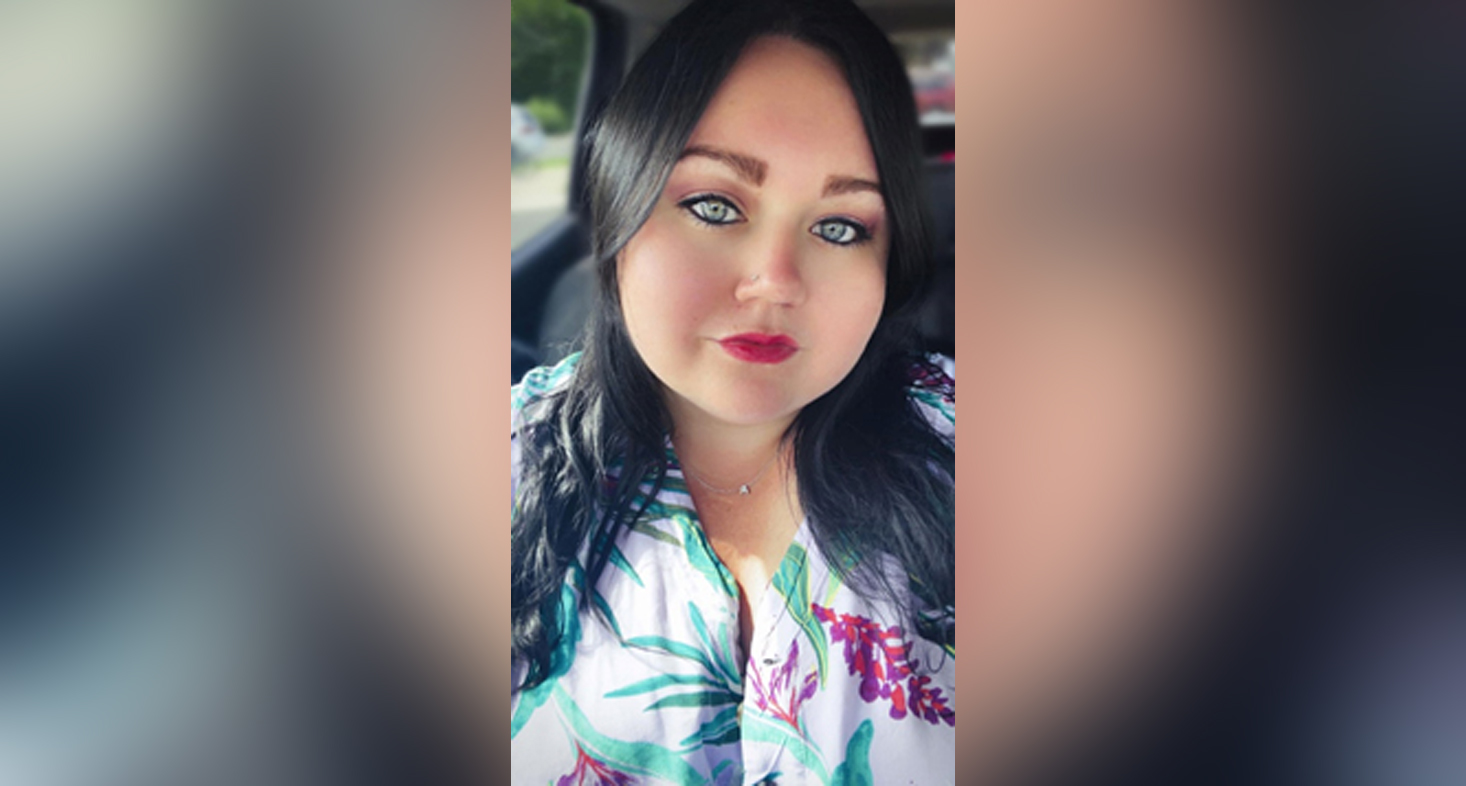
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Ashley Gladkowski

Rheumatoid arthritis is more common among women than men. About two to three times as many women as men have the disease. Ashley is one of those women.
Here is what Ashley has to say about her diagnosis.
“For me, it was scary hearing I had rheumatoid arthritis at age 22. I was so tired all the time and it took a while before I had even gotten a diagnosis. For a while, it was in remission. After I had covid in 2020, I spent a week in the hospital with pneumonia. My RA treatment stopped working and I switched to infusions. Some days, I forget how young I am because I feel trapped in my body. But it has made me stronger mentally and physically. I use my art to cope, and my experiences to do what I love as a mental health clinician. Now, at age 27 I’m finishing my master’s degree in psychology and not looking back” ~ Ashley Gladkowski #rheumatoidarthritis #rheumatoidarthritiswarrior #rheumatoidarthritisawareness.